Unit 6: Sensation (cont.)
|
TOUCH Touch or tactile sense involves a mixture of at least 4 distinct skin senses--pressure, warmth, cold, and pain. Only pressure has identifiable sense receptors. COLD + PRESSURE = WETNESS COLD + WARMTH = HOT PAIN Gate-Control-Theory: Theory that the spinal cord contains a neurological "gate" that blocks pain signals or allows them to pass. The gate is opened by stimulation of small nerve fibers and closed by stimulation of larger fiber or by information coming from the brain. TASTE Taste is the Gustatory Sense. Taste is a CHEMICAL SENSE and consists of the four basic tastes of sweet, sour, bitter, & salty. There may also be a 5th sense called "umami" or a meaty taste. Each bump on the tongue contains over 200 taste buds. Each bud contains a pore that captures food molecules. The molecules cause hair-like neurons within the pores to fire. Taste Buds reproduce themselves every 2-3 weeks.
SMELL Smells are processed in the temporal lobes of the brain and in the LIMBIC SYSTEM, which may explain why certain smells seem to have an emotional component and can trigger memories. |
Molecules in the air reach millions of receptor cells in each nasal
cavity. These cells send messages to the olfactory bulb and
the olfactory nerve which transmits the messages to the brain.
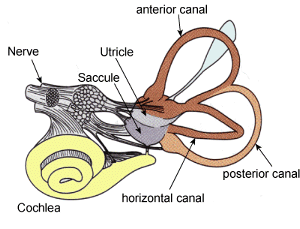
BODY POSITION & MOVEMENT Vestibular Sense: The system that monitors the head's
(and thus the body's) position and movement. It is our sense of
equilibrium.
|